Your cart is currently empty!
The Science of Oxalic Acid: Chemical Reactions and Uses
If you are preparing to work with oxalic acid, it is crucial to know the science behind it, its chemical reactions, and its uses. This organic compound has a molecular formula of C₂H₂O₄ and is naturally occurring in many plants, particularly leafy vegetables like spinach. Additionally, oxalic acid can be synthetically produced for industrial purposes. Keep reading to dive into the properties, chemical reactions, applications, and benefits of this fascinating compound.
What Is Oxalic Acid?
Oxalic acid, also known as ethanedioic acid, is a simple dicarboxylic acid. Many experts consider it to be the simplest dicarboxylic acid because it possesses two carboxyl groups. This organic compound exists in two forms: an anhydrous form, which is a colorless crystalline solid, and a dihydrate form, which appears as a white crystal.
Scientists can synthesize oxalic acid in laboratories, but it also naturally occurs in various sources. Plants, fungi, and even some animals can produce oxalic acid as a byproduct. This acid has a wide range of applications, including uses in the textile, pharmaceutical, and metal cleaning industries.
With its unique chemical properties, oxalic acid continues to intrigue researchers and scientists alike, contributing to our understanding of organic compounds and their potential applications.
Properties of Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid exhibits notable physical and chemical properties:
Solubility
Oxalic acid exhibits high solubility in water, which increases as temperatures rise. However, it shows limited solubility in organic solvents, such as ethanol and acetone, making it predominantly soluble in aqueous environments.
Acidity
Oxalic acid is considered a weak acid because it undergoes partial ionization in aqueous solutions. This process results in the generation of various ions.
Toxicity
Oxalic acid possesses toxic properties for humans due to its affinity for binding with calcium ions in the bloodstream, forming insoluble calcium oxalate crystals. These crystals can cause kidney damage and other health complications. Note that the lethal dose of oxalic acid for humans is around 15–30 grams, highlighting its significant and potent toxicity. When working with oxalic acid and its byproducts in a facility, make sure to label it as a dangerous substance in order to ensure you use it safely.
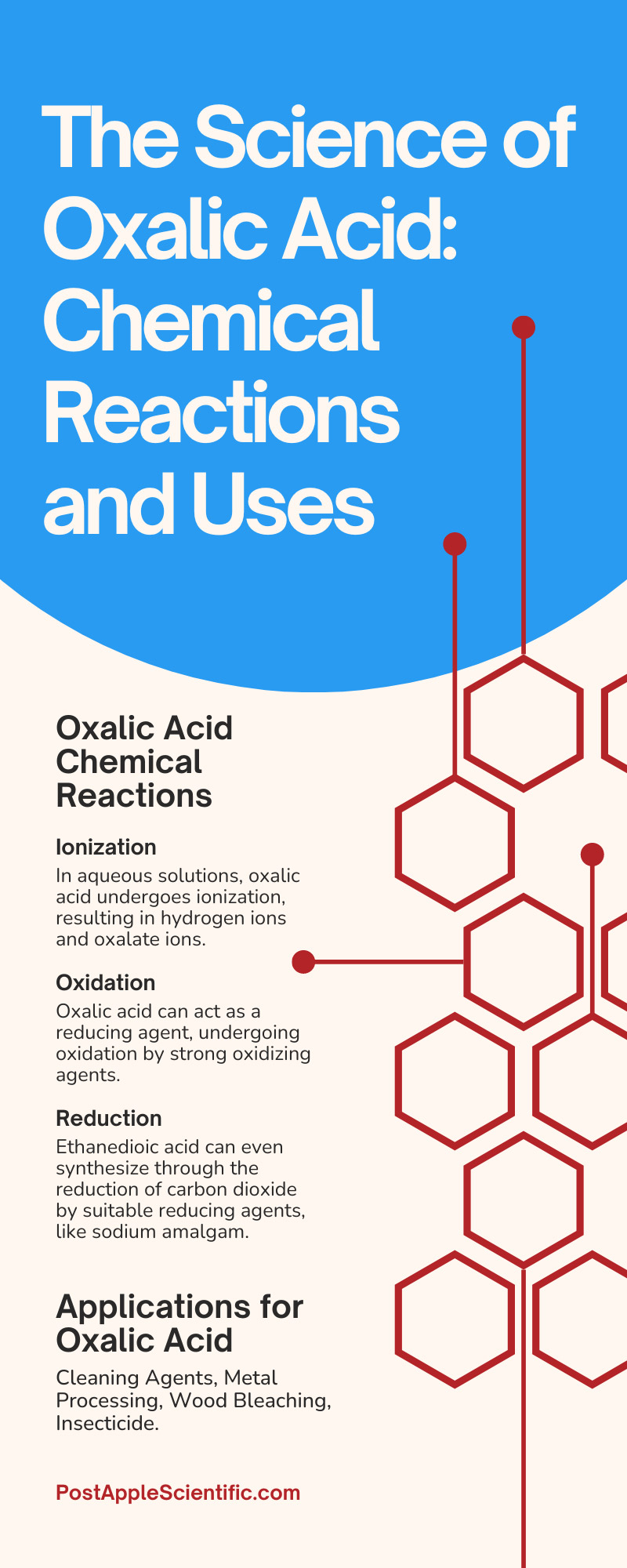
Oxalic Acid Chemical Reactions
Inducing chemical reactions with oxalic acid is essential for understanding its applications and behavior. Here are some key reactions:
Ionization
In aqueous solutions, oxalic acid undergoes ionization, resulting in hydrogen ions and oxalate ions. Ionization is crucial in many applications, such as the complexation of metal ions and analytical precipitation techniques.
Oxidation
Oxalic acid can act as a reducing agent, undergoing oxidation by strong oxidizing agents. It converts to carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) after oxidizing.
Reduction
Ethanedioic acid can even synthesize through the reduction of carbon dioxide by suitable reducing agents, like sodium amalgam.
Applications for Oxalic Acid
The versatility and unique properties of oxalic acid give rise to unique applications across various industries, including the following:
Cleaning Agents
Due to its acidic nature and exceptional chelating ability, ethanedioic acid is a powerful cleaning agent, particularly for removing stubborn rust or iron stains. Its descaling and decolorizing properties make it effective for restoring the shine of metal surfaces.
Metal Processing
Oxalic acid plays a crucial role in the metallurgical industry, where many experts use it for metal extraction, refining, and electroplating. By forming stable complexes with metal ions, oxalic acid facilitates the separation and purification of metals.
Wood Bleaching
Ethanedioic acid serves as a valuable ingredient in wood bleaching agents. Its unique ability to break down lignin and tannins in wood contributes to lightening the color and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of wooden objects and surfaces.
Insecticide
Oxalic acid exhibits potent insecticidal properties, making it a valuable substance for pest control. Specifically, it wards off pests like mites and aphids, safeguarding plants and promoting healthy growth.
These diverse applications highlight the significance of oxalic acid in various industries, showcasing its immense versatility.
Benefits of Using Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid also offers several benefits with its applications:
Eco-Friendly
As a naturally occurring compound, ethanedioic acid is biodegradable and does not harm to the environment like many synthetic chemicals. This makes it a sustainable substance for businesses looking to have a neutral impact on the environment. Because we can source oxalic acid from plants, we can consider it renewable and eco-friendly!
Cost-Effective
The widespread availability of oxalic acid in plants and its ease of synthesis make it a cost-effective compound for various industrial processes. Its low production cost and abundance in nature contribute to its affordability, making oxalic acid an attractive substance for businesses aiming to optimize expenses.
Versatile
The ability of oxalic acid to form stable complexes with metal ions gives it a wide range of applications in different industries, like metalworking. Professionals in this field can use oxalic acid as a cleaning agent, rust remover, and even as a reagent in chemical reactions. Its versatility opens up opportunities for innovation and creativity in various fields.
Where To Find Oxalic Acid
If you are looking to take advantage of oxalic acid for its many manufacturing or industrial applications, you might be wondering where to buy oxalic acid. Fortunately, you don’t need to look far when sourcing this compound and many other chemicals and solvents. At Post Apple Scientific, we supply chemicals and other materials for laboratories, manufacturers, and other facilities. Browse our online collection of reagents, including oxalic acid, for your unique applications.
Understanding the science of oxalic acid is vital for taking full advantage of its properties. From its discovery as a naturally occurring compound to its diverse array of synthetic uses, oxalic acid is a remarkably versatile substance in numerous industries. Its distinctive chemical reactions and benefits make it essential for scientific research.
As scientists delve deeper into the complexities of oxalic acid, new insights and applications are likely to emerge, further solidifying this compound’s significance in the realms of chemistry, materials science, and manufacturing. If you are looking for resources, don’t forget to browse Post Apple Scientific for reagents such as oxalic acid to meet your business’s chemical needs.
Leave a Reply